728x90
반응형
if
weather = "비"
weather = "미세먼지"
if weather == "비" :
print("우산 챙기세요")
elif weather == "미세먼지" :
print("마스크 챙기세요")
else :
print("날씨가 애매해요")
AND
temp = int(input("오늘 기온은 어때요?"))
if 30 <= temp :
print("더운 날")
elif 0 <= temp and temp < 10 :
print("날씨 좋은 날")
elif 0 <= temp < 10 :
print("외투를 챙기세요")
for
for waiting_no in [0,1,2,3,4] :
print("대기번호 : {0}".format(waiting_no))for waiting_no in range(5):
print("대기번호 : {0}".format(waiting_no))for waiting_no in range(1, 6):
print("대기번호 : {0}".format(waiting_no))
while
customer = "토르"
index = 5
while index >= 1 :
print("{0}, 커피가 준비 되었습니다. {1}번 남았어요".format(customer, index))
index -= 1
if index == 0 :
print("커피는 폐기 처분되었습니다.")
한줄 for 문
students = [1,2,3,4,5]
print(students)
students = [i+100 for i in students]
print(students)
배열 안에 글자 수를 길이로 변환
students = ["Iron man", "Thor", "I am groot"]
students = [len(i) for i in students]
print(students)
대문자로 변환
students = ["Iron man", "Thor", "I am groot"]
students = [i.upper() for i in students ]
print(students)[ 퀴 즈 ]
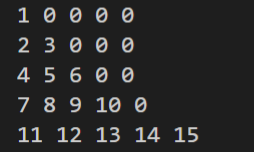
num1 = 1
for j in range(1,6) :
for a in range(j) :
print(num1 ,end=' ')
num1 += 1
for a in range(5-j) :
print("0",end=' ')
print()
함수
def aaa (a,b) :
return a,b
a, b = aaa(10,20)
print("a = " , a )
print("b = " , b )
def aaa (a,b) :
print("a는 {0} 이고 b는 {1}이다."\
.format(a,b) )
return a,b
a, b = aaa(10,20)
print("a = " , a )
print("b = " , b )
- '\' 를 사용하면 한 줄처럼 사용이 가능하다.
def aaa ( a, b="12" ) :
print("a는 {0} 이고 b는 {1}이다.".format(a,b) )
return a,b
a, b = aaa(10)
print("a = " , a )
print("b = " , b )
a, b = aaa(10,30)
print("a = " , a )
print("b = " , b )- 기본값을 지정해줄 수 있는데 매개변수가 존재할 경우에는 존재하는 값을 사용한다.
- 존재하지 않을 경우에는 지정해놓은 기본값을 사용 할 수 있다.
def aaa ( a, b ) :
print("a는 {0} 이고 b는 {1}이다.".format(a, b) )
return a,b
a, b = aaa( a=10, b=15 )
print("a = " , a )
print("b = " , b )
a, b = aaa( b=10, a=15 )
print("a = " , a )
print("b = " , b )- 매개변수의 이름을 직접 지정해 사용할 수도 있다.
가변인자
def aaa (a, b, *c) :
for lang in c:
print(lang , end=" ")
return a,b
a, b = aaa(100, 101, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)- 매개변수의 갯수를 유동적으로 바꿀 수 있다.
전역 변수 global
gun = 10
def aaa (a) :
# 전역 변수 gun을 사용하겠다
global gun
return gun-a
b = aaa(2)
print(b)sys
import sys
# 표준 출력
print("python", "java", file=sys.stdout)
# 표준 에러
print("python", "java", file=sys.stderr)
정렬 맞춰서 프린트
scores = {"수학":0, "영어":50, "코딩":12}
for subject, score in scores.items():
print(subject.ljust(8), str(score).rjust(4), sep=":")
10자리 공간 확보 후 Right 출력
print("{0: >10}".format(500))파일 다루기
- 파일 저장하기
score_file = open("score.txt", "w", encoding="utf8")
print("영어 : 99 ", file=score_file )
print("수학 : 88 ", file=score_file )
score_file.close()score_file = open("score.txt", "w", encoding="utf8")
score_file.write("과학 : 86")
score_file.write("음악 : 76")
score_file.close()
- 파일 전체 읽어오기
score_file = open("score.txt", "r", encoding="utf8")
print(score_file.read())
score_file.close()
- 파일 한 라인 읽어오기
score_file = open("score.txt", "r", encoding="utf8")
print(score_file.readline(),end="")
print(score_file.readline(),end="")
print(score_file.readline(),end="")
score_file.close()
- 파일 한 라인씩 whlie 로 읽어오기
score_file = open("score.txt", "r", encoding="utf8")
while True :
line = score_file.readline()
if not line :
break
print(line)
score_file.close()
- 파일 한 라인씩 for 로 읽어오기
score_file = open("score.txt", "r", encoding="utf8")
lines = score_file.readlines()
for line in lines:
print(line, end="")
score_file.close()
728x90
반응형
'TEAM STUDY > PYTHON' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 파이썬 웹 개발 입문 lv.2 (0) | 2020.12.24 |
|---|---|
| 파이썬 웹 개발 입문 lv.1 (0) | 2020.12.22 |
| 크롤링 시작하기 (0) | 2020.12.21 |
| 파이썬 기초1 (0) | 2020.12.19 |
| Python 스터디 계획 (0) | 2020.12.17 |


